CT Scan for Lung Cancer: Early Detection and Treatment Options
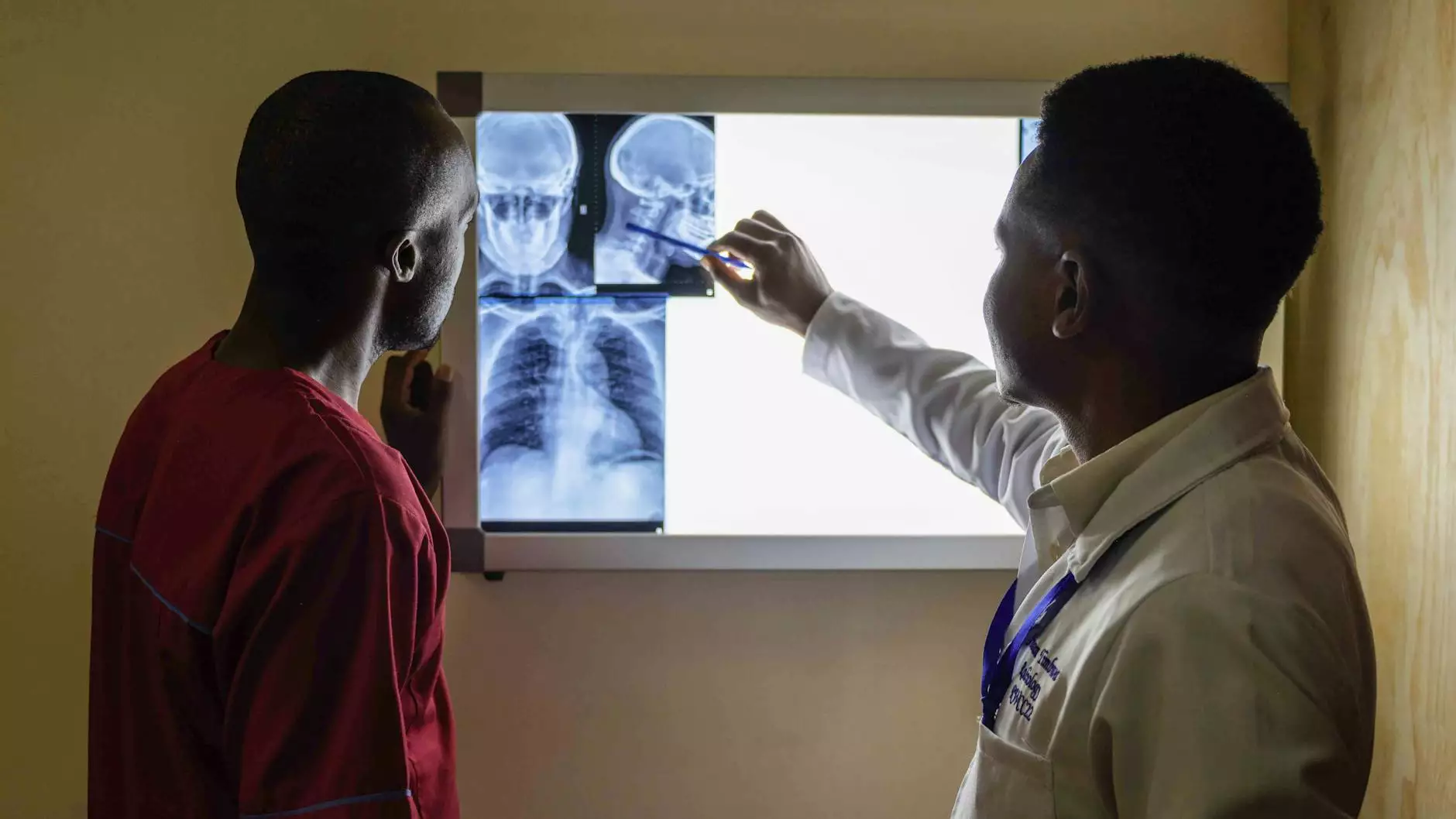
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. However, advancements in medical technology, particularly imaging techniques, have significantly improved early detection and treatment outcomes. This article delves deep into the role of CT scans for lung cancer, exploring how they work, their benefits, and their essential role in the broader context of lung health management.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer arises when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably. These cells can form tumors that interfere with lung function. The two primary types of lung cancer are:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) - accounting for about 85% of cases, this type grows more slowly and has better treatment outcomes.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) - more aggressive and tends to spread quickly, making early detection critical for effective treatment.
Key risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, asbestos, and air pollution, making awareness and early detection crucial for at-risk populations.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan (Computed Tomography scan) is an advanced medical imaging technique that utilizes X-rays to create detailed, cross-sectional images of the body. Unlike standard X-rays, which provide a two-dimensional view, CT scans produce three-dimensional images, allowing for a comprehensive look at internal structures.
The areas a CT scan can typically visualize include bones, organs, and blood vessels. This capability makes it an invaluable tool in diagnosing numerous medical conditions, including cancers.
The Importance of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Detection
When it comes to lung cancer, early detection is pivotal. A CT scan for lung cancer helps in:
- Early Diagnosis: Low-dose CT scans can detect lung cancer at an earlier stage compared to traditional X-rays. This is vital as early-stage lung cancer is often more treatable.
- Identifying Abnormalities: CT scans can reveal the presence of nodules or masses that may be indicative of lung cancer.
- Staging Lung Cancer: If diagnosed, CT scans help determine the cancer's stage, which is crucial for deciding on treatment options.
- Monitoring Treatment Response: CT scans can monitor changes in tumors during treatment, providing feedback on how well a treatment is working.
How Does the CT Scan Process Work?
When undergoing a CT scan for lung cancer, patients can expect a straightforward procedure:
Preparation
Patients may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours prior to the scan. It’s essential to inform the medical staff of any medications being taken or allergies, particularly to contrast materials.
The Scanning Procedure
- Patients will lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner.
- A technician will perform the scan, during which multiple images of the chest are captured from various angles.
- The entire procedure typically lasts about 10-30 minutes.
Post-Scan
After the scan, patients can resume their normal activities immediately. The images will be analyzed by a radiologist, and results are usually available within a few days.
Benefits of CT Scans for Lung Cancer Screening
The benefits of using CT scans in the context of lung cancer detection cannot be overstated. Some of the core advantages include:
- High Sensitivity: CT scans are extremely sensitive and can detect small nodules that may not be visible with a chest X-ray.
- Non-Invasive: A CT scan is a non-invasive procedure that does not require surgery or any invasive methods.
- Speed of Results: CT scans provide quick diagnostic results, allowing for timely management of the condition.
- Guidance for Further Testing: If abnormal findings are noted, CT scans can help guide subsequent biopsies or additional imaging.
Who Should Get a CT Scan for Lung Cancer?
Guidelines from health organizations recommend that certain populations undergo routine CT scans for lung cancer screening. These typically include:
- Adults aged 50-80 years.
- Individuals with a smoking history of 20 pack-years or more.
- Current smokers or those who have quit within the past 15 years.
It is crucial for individuals to discuss their specific risk factors with healthcare providers to determine the appropriate screening plan.
Limitations and Considerations of CT Scans
While CT scans are beneficial, several considerations must be taken into account:
- Radiation Exposure: Although low-dose CT scans significantly reduce radiation exposure, patients should always weigh the risks and benefits.
- False Positives: CT scans can sometimes identify nodules that may not be cancerous, leading to unnecessary anxiety and follow-up tests.
- False Negatives: There is also a chance that a CT scan may miss lung cancer, especially in its early stages.
Integrating CT Scans into Comprehensive Lung Health Management
A CT scan for lung cancer should be part of a larger framework of lung health management. This integrates preventive measures, lifestyle adjustments, and routine check-ups. Consider the following elements:
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking cessation is the most significant step in reducing lung cancer risk.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and potentially reduce cancer risk.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts immune function and promotes overall well-being.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine visits with healthcare providers can help manage lung health proactively.
Future Directions and Innovations in Lung Cancer Screening
The landscape of lung cancer screening continues to evolve with emerging technologies and methodologies. Innovations such as:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is increasingly being deployed to analyze CT scans for more accurate detection of lung cancer.
- Blood Tests: Research into liquid biopsies may provide non-invasive means to detect lung cancer markers in blood.
- Advancements in Imaging Technologies: Ongoing improvements in imaging technologies promise better resolution and faster results.
Conclusion: The Role of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Management
In conclusion, a CT scan for lung cancer is an indispensable tool in the fight against one of the most lethal forms of cancer. With its capability for early diagnosis and detailed imaging, it plays a crucial role not only in identifying lung cancer but also in monitoring treatment responses. As healthcare providers continue to refine screening processes, patients are encouraged to stay informed, take proactive steps in managing their lung health, and discuss the potential benefits of CT scanning with their healthcare teams.
By prioritizing early detection through CT scans and integrating comprehensive health strategies, individuals can enhance their chances of effective treatment and improved outcomes for lung cancer.