Molluscum Contagiosum
Skin Care
Welcome to the comprehensive guide to molluscum contagiosum, brought to you by Smith, Arthur F, MD in the field of Health.
Understanding Molluscum Contagiosum
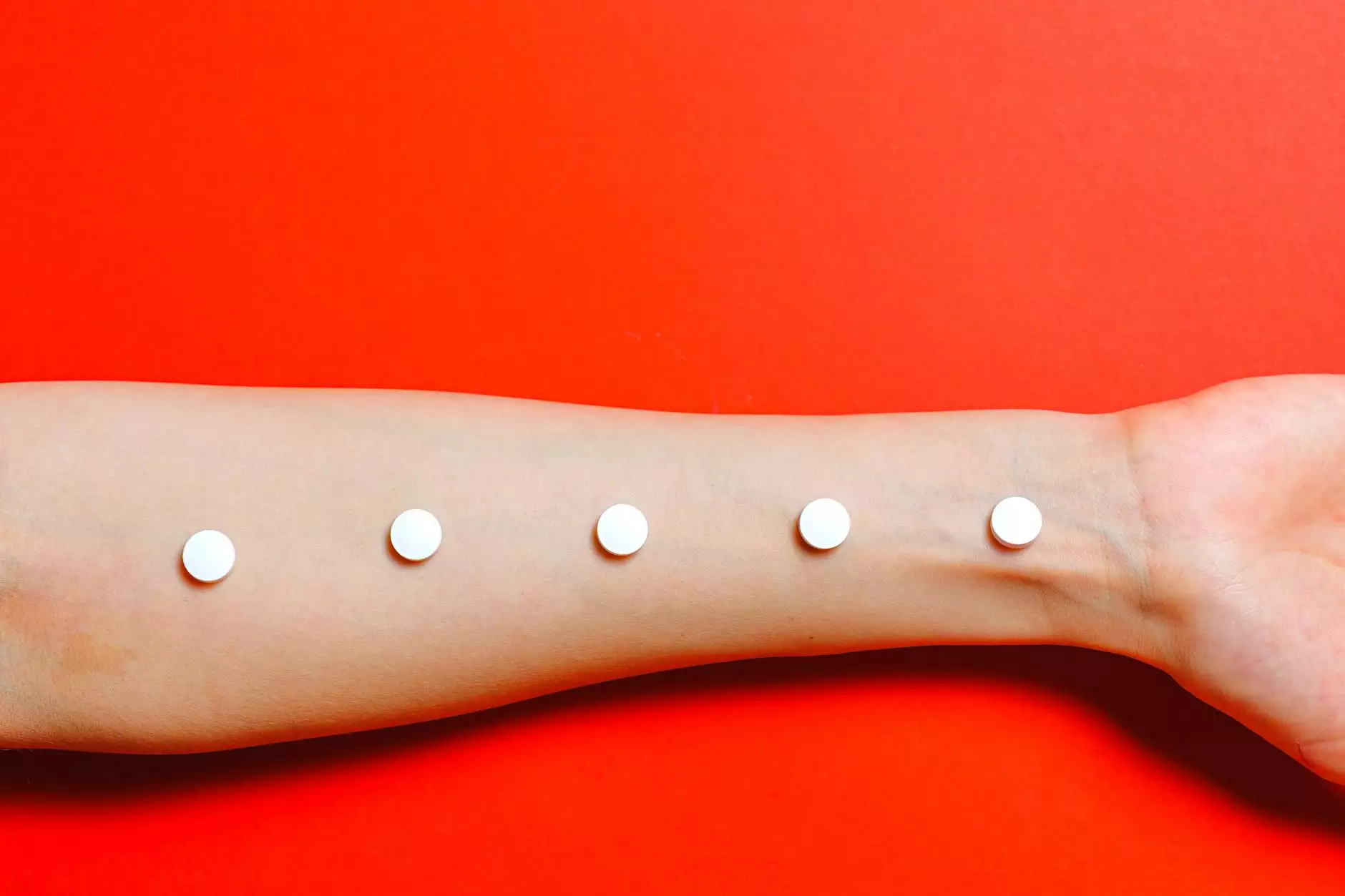
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection caused by a virus. It is characterized by small, raised bumps on the skin's surface. These papules may vary in color and can be flesh-colored, white, or pink. Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can easily spread through direct contact or touching contaminated objects.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptom of molluscum contagiosum is the appearance of small, painless papules on the skin. These bumps may be smooth, firm, and have a central indentation. They commonly appear in areas such as the face, neck, arms, and genitals, but can occur anywhere on the body. Other symptoms, such as itching or redness, may occur due to the body's immune response.
Diagnosing molluscum contagiosum usually involves a visual examination of the papules by a medical professional. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
Causes and Transmission
The molluscum contagiosum virus belongs to the poxvirus family and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. Common modes of transmission include sexual contact, sharing contaminated objects like towels or clothing, and scratching or picking at the papules, which can release the virus onto nearby areas of the skin.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, may be more susceptible to developing molluscum contagiosum.
Prevention and Control
While complete prevention may be difficult, there are several measures you can take to reduce the risk of contracting or spreading molluscum contagiosum:
- Avoid direct contact with infected individuals or their belongings.
- Practice good hand hygiene by washing your hands regularly with soap and water.
- Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, with others.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the papules to prevent further spread.
- Use barrier methods during sexual activity to reduce the risk of transmission.
Treatment Options
Molluscum contagiosum is generally a self-limiting condition, meaning it can resolve on its own over time. However, treatment may be recommended to prevent further spread, alleviate symptoms, or address cosmetic concerns. Some common treatment options include:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the papules with liquid nitrogen to destroy the infected tissue.
- Curettage: Scraping or scooping out the papules using a small, sharp instrument.
- Topical Treatments: Applying medicated creams or ointments directly to the affected areas to expedite healing.
- Cantharidin: A solution derived from a blister beetle that is applied to the papules to stimulate blistering and eventual removal.
- Laser Therapy: Using laser technology to target and destroy the papules.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the number and location of the papules, the age of the patient, and individual preferences. It is important to discuss treatment options and potential side effects with a qualified healthcare professional.
Outlook and Conclusion
Most cases of molluscum contagiosum resolve spontaneously within 6 to 12 months, even without treatment. However, it is essential to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management. Early detection and appropriate treatment can help minimize discomfort, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Remember, if you suspect you or your loved one may have molluscum contagiosum, consult Smith, Arthur F, MD for expert guidance and personalized care. We are dedicated to providing comprehensive healthcare services in the field of Health.